|
AH 321
Assessment of Athletic Injuries/Illnesses Laboratory
Joint & Soft
Tissue Palpation
| Hand & Wrist |
Arm |
Spine & Trunk |
Foot & Ankle |
| Forearm |
Shoulder
Girdle |
Hip, Knee &
Lower Leg |
Head & Face |
|
back
to AH 321 |
| |
|
|
|
FOOT & ANKLE
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
| 1st Interphalangeal joint |
|
Patient sitting or standing with the foot in neutral. |
It is located on the great toe and it is the joint just
proximal to the toe nail. |
|
 |
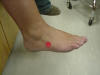
| 5th Metatarsocuboid |
|
Foot in neutral position |
Located on the lateral side of the ball of the foot; the
joint is located inferior to the 5th metatarsal and superior to the cuboid. |
|
 |
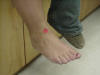
| Anterior Inferior Tibiofibular |
Amphiarthrodial; The anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament
lies just superior to the joint. |
Clear palpation is impossible because the anterior inferior
tibiofibular ligament overlies the joint; You can only feel a slight
depression over it. |
Located immediately proximal to the talus. |
|
 |
| 4th DIP |
The attachment of flexor digitorum longus, extensor
digitorum longus, and it is formed by the 4th distal phalanx and the 4th
middle phalanx. |
The patient's foot needs to be in neutral and relaxed. |
It is the distal joint on the fourth metatarsal. |
|
 |
| Talocrural (anterior) |
|
|
|
|
_small.JPG) |
| Talocrural (posteromedial) |
Allows foot to
dorsiflex and plantarflex; flexor hallucis longus crosses this joint |
Short-sitting, foot
in neutral |
Immediately
posterior to the medial malleolus |
(S)_small.JPG) |
|
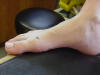
| 1st Metatarsophalangeal |
Joint most involved
in gout, bunions, and "turf toe"; extensor hallucis longus
crosses this joint |
Short-sitting, foot
in neutral |
Located on the
anteromedial side of the foot; where the head of the 1st metatarsal
articulates with the proximal head of the 1st proximal phalanx |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| Talonavicular |
Articulation point
of the talus and navicular; it is a midtarsal joint |
Short-sitting
position, foot relaxed |
Located medially
and proximal to the navicular tubercle |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| Posterior Inferior Tibiofibular |
Posterior inferior
tibiofibular ligament crosses this joint and serves to keep the mortise
from widening |
Short-sitting, foot
in neurtal |
Posterior and
distal articulation of the tibia and fibula |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| 5th MP |
|
|
|
_small.JPG) |
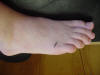 |
| Calcaneocuboid |
Serves as an
attachment for the peroneus brevis muscle |
Patient in
short-sitting position, foot in neutral |
It is lateral to
the talus and cuneiforms |
|
|
| Talocrural (posterolateral) |
Ginglymus joint |
Patient in short
sitting position with foot in neutral |
The talocrural
controls dorsiflexion and plantarflexion |
|
|
| 3rd PIP |
Sliding joints |
Patient in
short-sitting position, foot in neutral |
It is located
distally to the third proximal phalanx |
|
|
| Subtalar |
Subtalar joint
controls the movements of inversion, eversion, pronation, and supination |
Patient in
short-sitting position with foot in neutral |
Subtalar joint is
located inferior to the lateral malleolus |
|
|
LOWER LEG
RIB & SPINE
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
| Posterior Intervertebral Joints C2-S1 |
Spaces for spinal nerves to pass through to supply the body. |
The patient must be lying prone. |
Located from the base of the skull to the posterior superior
iliac spine. |
|
 |
| Posterior Rib #8 & T8 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Anterior Rib #4 & sternum |
|
|
You can locate these bones by moving up from the xiphoid
process approximately three finger widths; this is where the two bones
connect. |
|
|
| Posterior Rib #1 & T1 |
A true rib;
connected to the manubrium by costal cartilage; lies directly inferior to
the clavicle. |
The patient must be
lying prone with some capital and cervical flexion |
The first
rib-thoracic vertebrae articulation located inferior to the prominent
spinous process of C7 |
|
|
| Posterior Rib #12 & T12 |
Attachment site of
erector spinae muscle |
Prone |
Where the posterior
head of rib 12 articulates with the transverse process of T12 |
|
|
| Anterior Rib #7 & Sternum |
Where the serratus
anterior attaches |
Patient in supine |
Located on the
ventral side of the abdomen between the 6th and 7th ribs |
|
|
| Posterior Rib #4 & T4 |
Arthrodial
joints |
Patient standing
relaxed or lying prone |
Where the posterior
aspect of rib 4 articulates with the transverse process of T4 |
|
|
| Anterior Rib #2 & Sternum |
Where the
pectoralis major attaches |
Patient standing
relaxed or lying supine |
Where the anterior
aspect of rib 2 articulates with the sternum |
|
|
HIP
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
| Posterior Sacroiliac |
Posterior
sacroiliac ligaments attach here |
Prone |
Where the posterior
sacrum articulates with the posterior iliac spine |
_small.JPG) |
 |
SHOULDER
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
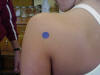
| Posterior Glenohumeral |
Apex of the pyramid that is formed by the axilla |
Patient sitting with arm adducted and elevated at 45 degrees |
Located posteriorly to the glenohumeral joint, resting on
the superior scapula border |
|
 |
| Acromioclavicular |
Movement can be felt when the patient actively flexes and
extends; Arthrodial joint |
Palpation is easier if the patient rotates the arm, push in
a medial direction against the thickness at the end of the clavicle |
Find the clavicle and palpate laterally to the distal most
point. |
|
 |
| Anterior Glenohumeral |
Site where the
glenoid labrum encapsulates the humeral head |
Patient supine;
externally rotate the shoulder, palpate the acromion and move slightly
distal |
Anterior surface of
the shoulder where the head of the humerus articulates with glenoid fossa |
_small.JPG) |
 |
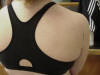
| Inferior Glenohumeral |
Attachment site of
inferior glenohumeral ligament |
Patient supine, arm
abducted to at least 90° |
Where the inferior
portion of the humeral head articulates with the inferior rim of the
glenoid fossa |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| Sternoclavicular |
Enarthrodial joint
supported by the anterior sternoclavicular ligament |
Either standing in
the anatomical position or in short sitting position |
Located lateral to
the suprasternal notch |
|
|
| Superior Glenohumeral |
Enarthrodial joint
that is supported by the joint capsule, glenoid labrum, and the
coracohumeral ligament |
Patient in the
short-sitting position with shoulder relaxed |
Where the superior
aspect of the humeral head articulates with the glenoid fossa |
|
|
ELBOW & FOREARM
WRIST
HAND
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
| 1st Metacarpophalangeal |
Condyloid type joint |
MCP joint flexed |
Located immediately distal to the 1st metacarpal bone |
|
 |
| 2nd PIP |
Extensor indicis, extensor digitorum, flexor digitorum
superficialis, and is composed of the 2nd middle phalanx and the 2nd
proximal phalanx |
Neutral |
Located just inferior to the 2nd metacarpal joint. |
|
 |
| 3rd DIP |
Hinge joint |
To palpate find the third finger on the hand, and make sure
the model's hand is relaxed on the table. |
Palpate until the last joint of the finger just proximal to
the nail. |
|
 |
| 1st Carpometacarpal |
Extensor pollicis
longus and brevis cross this joint |
Hand in full
pronation, resting on table; ask the model to oppose the thumb and palpate
the joint line |
Where the trapezium
articulates with the 1st metacarpal |
_small.JPG) |
 |
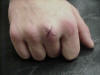
| 3rd Metacarpophalangeal |
Where flexion,
extension, abduction, and adduction occurs in the 3rd phalange |
Han in full
pronation, resting on table |
Where the head of
the 3rd metacarpal articulates with the proximal head of 3rd proximal
phalanx |
|
 |
| 2nd DIP |
Joint has only
flexion and extension; has reinforcing collateral ligaments on medial and
lateral joint lines |
Hand and forearm
resting on table with the fingers hanging over the edge |
Where the distal
head of the intermediate phalanx of the index finger articulates with the
proximal head of the distal phalanx |
|
|
| 3rd Metacarpal-Capitate |
Condyloid joint |
Hand in pronation,
resting on table |
This joint performs
the movements of flexion,extension, abduction, adduction, and
circumduction |
|
|
| 5th Metacarpophalangeal |
Site of finger
abduction, adduction, and MCP flexion and extension |
Palm and forearm
resting on flat surface |
Where the head of
the 5th metacarpal articulates with the proximal end of the proximal
phalanx |
|
|
| 4th PIP |
Condyloid joint |
Hand in pronation,
resting on table |
This joint is
located distal to the MCP joint |
|
|
FACE
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
| Anterior Temporomandibular |
Attachment site of
the auricularis muscle |
Patient in supine;
instruct patient to open and close the mouth while the examiner palpates
the joint line |
Posterior and
lateral to the zygomatic arch and anterior to the external ear canal |
_small.JPG) |
|
| Posterior Temporomandibular |
Serves as an attachment for the
Stylomandibular ligament |
Patient is short sitting and
relaxed |
The joint is inferior to the
external auditory meatus |
|
|
SOFT TISSUE
KNEE
FOOT & ANKLE
THORAX
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
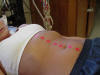
| Linea Alba |
|
The patient can be seated or lying supine on a table and
relaxed. |
With the abdominal muscles contracted, this is the verticle
line that runs between the left and right rectus abdominis muscles. |
|
 |
NECK
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
| Sternocleidomastoid Muscle |
Located lateral to
the thyroid cartilage |
Turn head to the
opposite side of the side that is being palpated |
Extends from the
sternoclavicular joint to the mastoid processes |
|
|
ELBOW
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
| Distal Biceps Brachii Tendon |
Located in the cubital fossa |
Arm flexed to 90 degrees |
Located distally from the belly of the bicep muscle.
It attaches proximally along the radial tuberosity. When the arm is
flexed the tendon becomes prominent at the bend of the elbow. It is
bordered laterally by the brachioradialis and medially by the pronator
teres |
|
 |
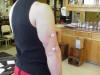
| Distal Triceps Brachii Tendon |
Connects the
triceps muscle to the proximal end of the olecranon process |
Have patient
standing with the arm internally rotated, elbow flexed, with the
hand supported; palpate on the proximal end of the olecranon process |
Located on the
posterior side of the arm and attaches to the olecranon process |
|
 |
| Ulnar Collateral Ligament |
Stabilizes the
elbow to prevent valgus instability |
Patient in short
sitting position with arm externally rotated |
Located on the
medial side of the arm and attaches into the medial epicondyle |
|
|
HAND
Joint or Soft
Tissue Structure
(include alternative name if applicable) |
Related
Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved |
Preferred
Body & Joint Position
best for palpation |
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures |
Skeleton
Picture or Video |
Model Picture or Video
|
| Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon |
It is the ulnar border of the anatomical snuffbox |
Hand in neutral position |
Tunnell III on the ulnar side of the radial tubercle. |
|
 |
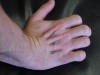
| Extensor Digitorum Tendon |
|
|
|
|
 |
|