|
Bony Landmark
(include alternative name if applicable)
|
Related Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved
|
Preferred Body & Joint
Position
best for palpation
|
Anatomical Description of Location
relative to other structures
|
Skeleton Picture or Video
|
Model Picture or Video
|
| Sesamoid bones |
Distributes some of the
weight-bearing pressure, provides mechanical advantage for the flexor
tendon of the great toe |
Foot in neutral |
Located distally along the
medial longitudinal arch past the base of the 1st metatarsal bone to the
1st metatarsophalangeal joint |
 |
 |
| Sinus tarsi |
Contains the extensor
digitorum brevis muscle; has an overlying fat pad |
Short-sitting, foot relaxed |
Anterior to the lateral
malleolus |
_small.JPG) |
 |
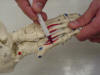
| 5th metatarsal
shaft |
Serves as the attachment for
the interphalangeal joints of the foot |
Patient sitting on the edge
of the table with legs relaxed |
Located on the lateral side
of the foot just superior to the cuboid bone |
 |
 |
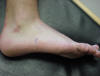
| 5th metatarsal
base |
Also known as the styloid
process; Is the insertion point for the peroneus tertius, peroneus brevis,
and the tibialis posterior muscle |
Foot in neutral, or sitting
position |
Located on the lateral side
of the foot distal to the cuboid bone |
 |
 |
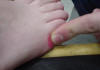
| 5th metatarsal
head |
Provides support to the
lateral foot |
Short-sitting with talocrural
joint in neutral and phalanges in extreme extension |
The distal end of the most
lateral metatarsal |
_small.JPG) |
 |
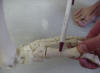
| 1st metatarsal
shaft |
Insertion for tibialis
anterior muscle and attachment for flexor hallucis longus tendon |
Patient sitting on edge of
table with legs relaxed |
Located just proximal to
first MP joint |
 |
 |
| 3rd metatarsal
head |
Morton's neuroma occurs
between the 3rd and 4th metatarsal heads |
Foot in neutral |
Located distally by placing
the thumb upon the plantar surface and your index finger upon the dorsal
surface, located immediately in front of the transverse arch, and just
distal to the 3rd distal phalanx |
 |
 |
| 1st metatarsal
base |
Articulates with medial
cuneiform; site of insertion of tibialis anterior tendon |
Short-sitting position |
Proximal portion of 1st
metatarsal |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| 1st metatarsal
head |
Serves as the attachment for
the extensor hallucis longus tendon |
Patient sitting on edge of
table with legs relaxed |
Located inferiorly to the
first MP joint |
 |
 |
| Medial cuneiform |
Assists in the gliding motion
of the foot |
Patient seated with foot
relaxed |
Start on the inside of the
foot with the great toe, palpate until you come to the 1st metatarsal, the
metatarsal flares slightly at its base until it becomes the 1st cuniform,
from the 1st cuniform move laterally until you palpate the next bony
prominence (medial cuniform) |
 |
 |
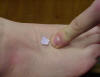
| Intermediate cuneiform |
Attachment site of the dorsal
metatarsal ligaments |
Short-sitting position with
talocrural joint relaxed |
Lies between the medial and
lateral cuneiforms and proximal to the 2nd metatarsals |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| Lateral cuneiform |
The lateral cuneiform is
directly connected to the cuboid bone by way of the dorsal cuneocuboid
ligament located anteriorly |
The patient should be sitting
with legs hanging off the edge of table and relaxed |
The lateral cuneiform is
located on the lateral aspect of the foot medial to the cuboid bone |
 |
|
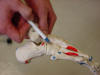
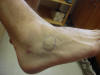
| Cuboid |
It is the site of attachment
for the dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament |
Patient seated with the foot
relaxed |
Located directly distal to
the calcaneous bone |
 |
 |
| Navicular |
Articluates with the talus
and 3 cuneiform bones; tibials posterior attaches to the navicular
tubercle |
Short-sitting, foot relaxed |
Midway between the calcaneus
and the base of the 1st metatarsal |
 |
|
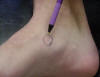
| Navicular tubercle |
Attachment for tibialis
posterior tendon and spring ligament |
Patient sitting on edge of
table with legs relaxed |
Bony prominence located along
the medial border of the foot, proximal to the medial cuniform and distal
to the talar head |
|
 |
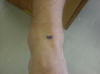
| Talar dome |
Only a small portion of the
dome can be palpated, a greater portion of its surface is palpable on its
lateral side than on the medial side; It allows for anterior and posterior
rocking which causes plantarflexion and dorsiflexion to occur |
Can be palpated with the foot
in inversion and plantarflexion; the patient needs to be seated |
Palpate just inferior and
medial from the lateral maleolus; you can only feel a portion of the talar
dome |
 |
 |
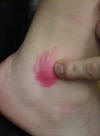
| Lateral malleolus |
Serves as a pulley for the
tendons & muscles that lie posteriorly to it; site of attachment of
the anterior and posterior talofibular ligaments that attach the talus and
fibula; site of attachment of the anterior and posterior tibiofibular
ligaments that attach the tibia and fibula |
Short-sitting position
|
Distal end of the fibula |
_small.JPG) |
 |
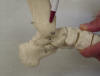
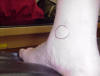
| Medial malleolus |
Serves as an attachment for
the Deltoid Ligament |
Patient sitting on the edge
of the table with leg flexed 30 degrees and the patient being relaxed |
Located at the distal end of
the tibia |
 |
 |
| Tibial plafond |
Anterior tibiofibular
ligament and anterior joint capsule connect to the tibial plafond |
Foot plantar flexed |
Located on the distal surface
of the tibia |
 |
 |
| Calcaneus |
Supports weight transmitted
from the talus during walking and running; the ligaments that attach there
are the tendo calcaneus, dorsal calcaneocuboid, interosseous talocaneal,
calcaneofibular, tibiocalcaneal, plantar calcaneonavicular, medial
talcalcaneal, and posterior talocalcaneal; the muscles that attach are the
gastrocnemius, extensor digitorum brevis, flexor digitorum brevis, soleus,
abductor hallucis, and abductor digiti minimi brevis |
Short-sitting with foot in
neutral position |
Distal to the lateral
malleolus; lies beneath the talus |
_small.JPG) |
|
| Peroneal tubercle |
Separates the peroneus brevis
and peroneus longus tendons at the point where they pass around the
lateral calcaneus |
Patient sitting on edge of
table with feet hanging over and relaxed |
Located on calcaneus, distal
to the lateral malleolus |
XX |
 |