|
Bony Landmark
(include alternative name if applicable)
|
Related Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved
|
Preferred Body & Joint
Position
best for palpation
|
Anatomical Description of Location
relative to other structures
|
Skeleton Picture or
Video
|
Model Picture or Video
|
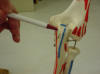
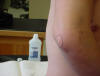
| Olecranon process |
Attachment for triceps brachii tendon |
Patient with arm at side, elbow flexed
approximately 30 degrees |
Bony prominence of
the proximal ulna,
just distal to the olecranon fossa and lateral to the medial epicondyle of
the humerus |
 |
 |
| Tuberosity of the radius |
Insertion of the
biceps brachii tendon |
Elbow flexed at 90
degrees |
Follow the biceps
brachii muscle and tendon distally to the radius; once you lose the tendon
the tuberosity lies just underneath your finger or thumb |
|
|
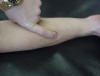
| Radial shaft in supination |
Attachment of
interosseous membrane, pronator quadratus, and wrist flexors |
Sitting with arm in
supination |
Lateral forearm |
 |
 |
| Medial supracondylar ridge |
Serves as an attachment for the flexor muscles
of the wrist |
Patient standing with the elbow flexes 30
degrees |
Located superior to the medial epicondyle of
the humerus |
|
|
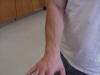
| Radial shaft in pronation |
Also called the
forearm |
Patient needs to be
standing or seated with the elbow flexed at 90 degrees and then rotate the
shaft laterally |
It attaches to the
elbow (olecranon fossa) and it articulates with the capitellum and humerus
on its distal end |
 |
 |
| Ulnar shaft in supination |
Origin of flexor
digitorum profundus and pronator quadratus |
Arm resting on
table, anatomic position |
Medial forearm in
anatomic position |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| Ulnar shaft in pronation |
Serves as an attachment for the interosseous
membrane |
Patient lying in the prone position with the
arm relaxed |
When in pronation, the ulna will be located on
the lateral side of the forearm. Crosses over the radius in pronation |
 |
|
| Lateral supracondylar ridge |
The site of the
wrist extensors or the "mobile wad of 3" the brachioradialis,
extensor carpi radialis longus, and the extensor carpi radialis brevis;
also the brachioradialis originates from here |
Stand at the
patient's side and hold the anterior lateral aspect of the arm, move
upward in a linear fashion from the lateral epicondyle, and palpate a
short bony ridge, palpate up and down the ridge to get a good feel for its
prominence |
Located on the
posterior distal end of the humerus above the lateral epicondyle |
 |
 |
| Styloid process-radius |
Reference point of
carpal palpation; insertion of brachioradialis |
Forearm relaxed on
table |
Distal tip of
radius |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| Styloid process-ulna |
The extensor carpi ulnaris tendon runs thru a
groove in the distal tip of the ulna styloid process |
Patient standing, relaxed |
The ulna styloid process is located both
medially and posteriorly on the wrist in the anatomic position |

XXX |
|
| Tubercle of the radius (Listerís Tubercle) |
When the hand is
broken down into zones the tubercle of the radius makes up the 2nd zone |
Have the patient's
hand and wrist in a neutral position |
It is the bony
ridge located between the ulna and radius on the posterior and distal
aspect of these two bones, between the ulna and radius distally |
Skeleton_small.JPG) |
Body_small.JPG) |