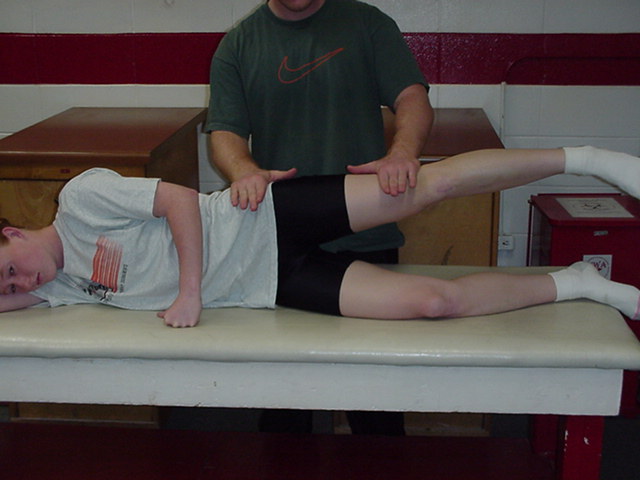
| Hip Abduction |
The patient is side lying with test leg
uppermost. The therapist stands behind the patient and stabilizes with one
hand at the hip. This hand is proximal to the greater trochanter. The
other hand applies resistance across the lateral surface of the knee.
Patient abducts hip against downward resistance. |
 |
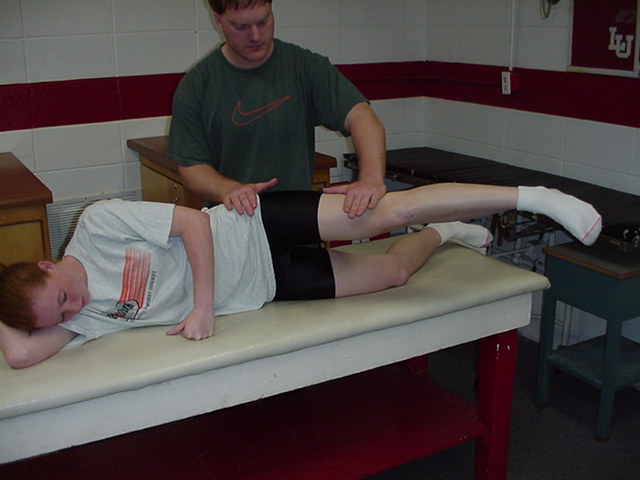
| Hip Abduction
Flexed |
The patient is side
lying with test leg uppermost, and hip flexed to 45 degrees. The therapist stands behind the patient and stabilizes with one
hand at the hip. This hand is proximal to the greater trochanter. The
other hand applies resistance across the lateral surface of the knee.
Patient abducts hip against downward resistance. |
 |
| Hip Adduction |
The patient is side
lying with the test leg lowermost and resting on the table. The uppermost
leg is abducted to 25 degrees and supported by the examiner. The therapist
stands behind the patient at the knee level. The resistance hand is placed
on the distal medial femur of the test leg. Resistance is applied in a
downward motion while the patient actively adducts. |
 |
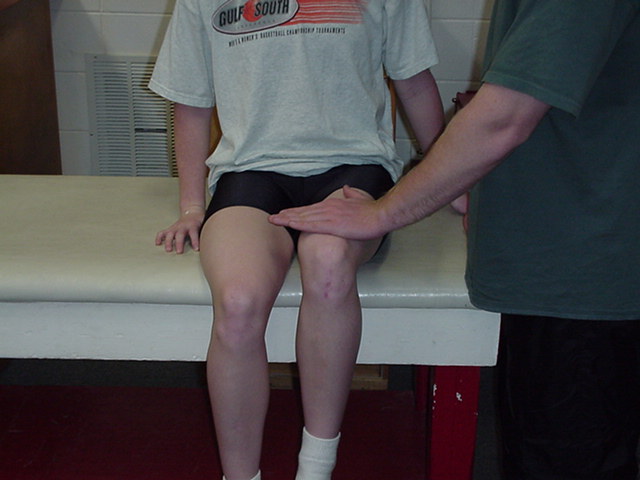
| Hip Flexion |
The patient is
short sitting with thighs fully supported and legs hanging over the edge.
The therapist stands next to the test leg. The therapist places one hand
on the distal thigh and proximal knee, and applies resistance in a
downward direction as the patient actively flexes at the hip |
 |
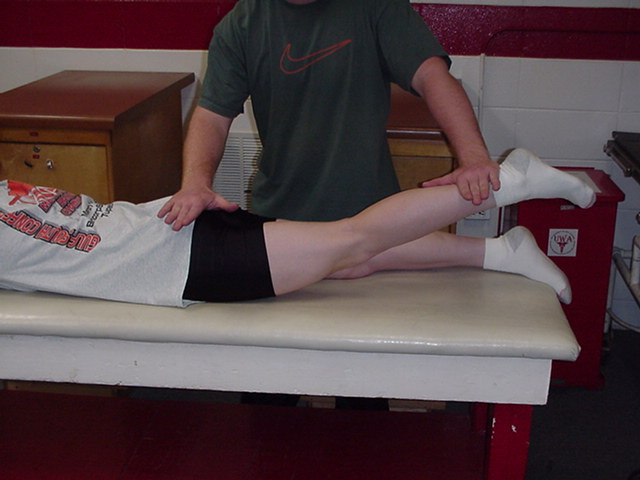
| Hip Extension |
The patient lies
prone on the table. The therapist stands on the side of the test leg, at
pelvis level. One hand stabilizes the pelvis, and the other hand is placed
on the distal calf. The hand on the distal calf applies resistance in a
downward direction ad the patient actively extends at the hip. |
 |
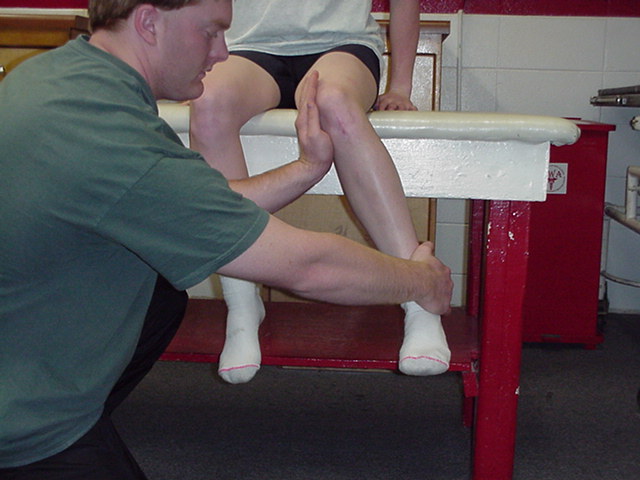
| Hip Internal
Rotation |
The patient is
short sitting. The therapist sits on a stool or kneels beside patient. The
therapist places one hand at the medial aspect of the distal thigh and
applies resistance in a lateral direction. The other hand grasps the
lateral ankle just above the malleolus, and applies resistance in a medial
direction. The patient is actively internally rotating at the hip. |
 |
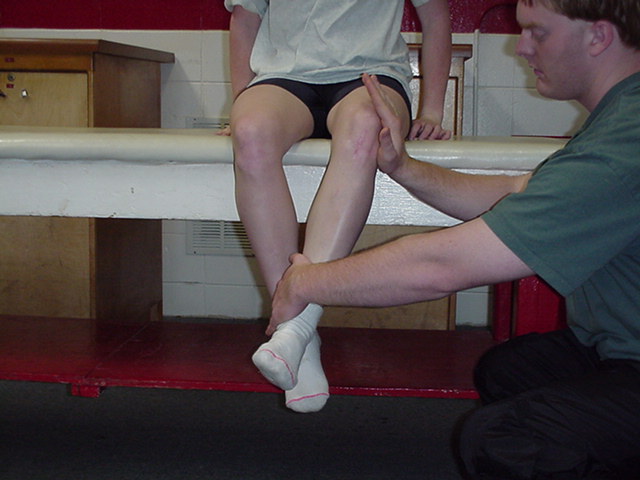
| Hip External
Rotation |
The patient is
short sitting. The therapist sits on a stool or kneels beside patient. The
therapist places one hand at the lateral aspect of the distal thigh and
applies resistance in a medial direction. The other hand grasps the medial
ankle just above the malleolus, and applies resistance in a lateral
direction. The patient is actively externally rotating at the hip. |
 |
| Hip Flexion
Abduction Ext. Rotation |
The patient is
short sitting with thighs supported on table and legs hanging over side.
The therapist stands lateral to the test leg while placing one hand on the
lateral side of the knee and using the other hand to grasp the medial
anterior surface of the distal leg. Hand at knee gives downward and inward
resistance. Hand at ankle gives upward and outward resistance. Patient
flexes, abducts, and externally rotates the hip and flexes the knee. |
 |
Hislop, Helen J. & Montgomery, Jaqueline with
contributor Barbara Connelly.







