|
Bony Landmark
(include alternative name if applicable)
|
Related Information
such as purpose, function,
attachment of ligaments, tendon, soft tissues involved
|
Preferred Body &
Joint Position
best for palpation
|
Anatomical
Description of Location
relative to other structures
|
Skeleton Picture or Video
|
Model Picture or Video
|
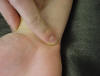
| Pisiform |
Along with the
hamate, it permits passage of the ulnar nerve and artery; the flexor carpi
ulnaris and abductor digiti minimi attach here; also attachment site of
pisohamate ligament |
Arm and hand
resting on table in the anatomical position |
On the ulnar side
of the wrist, just proximal to the base of the 5th metacarpal |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| Scaphoid (navicular) in snuffbox |
The navicular forms the floor of the anatomic
snuffbox. The rest of the snuffbox is formed by the abductor pollicis
longus and the extensor pollicis longus and brevis tendons |
Patient needs to be sitting on the edge of the
table with arm relaxed and abducted, with the thumb extended laterally
away from the fingers |
The anatomic snuffbox is a small depression
located immediately distal and slightly dorsal to the radial styloid
process |
 |
 |
| Scaphoid tubercle |
Also called the
"navicular" |
Patient's hand
relaxed on the table |
It is situated on
the radial side of the carpus, longest bone in the proximal carpal row,
ulnar deviation causes the navicular to slide out from under the radial
styloid process so that it becomes palpable |
 |
 |
| Triquetrum |
Vulnerable to
injury, ranking 3rd highest of all the carpal bones in incidence of a
fracture |
Hand must be
radially deviated or abducted so the triquetrum moves from under the
styloid process |
Lies just distally
to the ulnar styloid process, in the proximal carpal row |
 |
 |
| Trapezoid |
|
Hand relaxed on
table, palm side down |
Lies between the
capitate and trapezium |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| Capitate |
Attachment for capitotriquentral ligament |
Patient's wrist in neutral position |
Located in the depression just proximal to the
base of the 3rd metacarpal and distal to Lister's tubercle |
 |
XX |
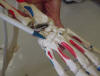
| Hamate |
Forms the insertion
of part of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle |
Patient's hand
supported by the examiner with the forearm and wrist in supination |
Is located slightly
distal and radial to the pisiform; place the interphalangeal joint of your
thumb upon the pisiform, pointing the tip of your thumb toward the web
space between the patient's thumb and index finger and rest the tip of
your thumb in the palm of the patient's hand, the hammate lies directly
underneath the tip of your thumb, but is hard to palpate because it is
buried deeply under layers of soft tissues |
 |
 |
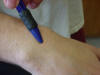
| Lunate |
Articulates
proximally with the radius and distally with the capitate; covered by the
extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon; most frequently dislocated and 2nd
most fractured bone of the wrist |
Wrist in flexion |
Follow the 3rd
metacarpal to its articulation with the capitate; there will be an
indention; have the patient flex the wrist; this will make the lunate
palpable |
_small.JPG) |
 |
| Hamate (hook) |
Forms the lateral border of the tunnel of Guyon
which transports the ulnar nerve and artery to the hand |
Patient sitting on the edge of the table,
relaxed |
Located slightly distal and radial to the
pisiform |
 |
 |
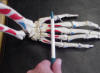
| Metacarpals 1-5 |
Insertion point for
the flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis,
extensor carpi radialis longus, and adductor pollicus longus |
Hand relaxed and in
a neutral position |
Located superior to
the phalange bones |
 |
 |
| Metacarpal heads 1-5 |
Attachment site of
flexor digitorum superficialis |
Fingers in full
extension |
Articulates with
base of proximal phalanx |
 |
 |
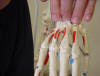
| Metacarpal bases 1-5 |
Assist in flexion and extension of the fingers |
Patient's wrist in neutral position |
Located superiorly to the carpal bones |
 X X |
 X X |
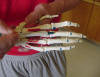
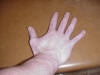
| Proximal phalanxes 1-5 |
Classified as
ginglymus joint |
Hand supinated or
in anatomical position |
Located between the
distal phalanxes and the MCP joint respectively 1-5 |
 |
 |
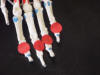
| Middle phalanxes 2-5 |
Insertion of flexor
digitorum superficialis and extensor indicis muscles |
Hand supinated and
fingers extended |
Lies between
proximal phalanx and distal phalanx |
 |
 |
| Distal phalanxes 1-5 |
serves as attachments to the DIP joint |
Patient sitting on table and relaxed |
Located superior to the DIP joint |
 |
 |